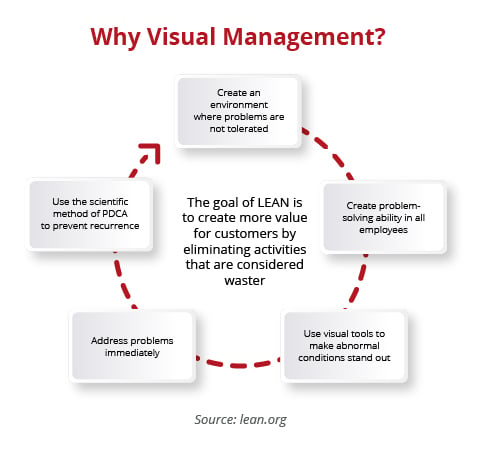
Visual Management is a management technique that aims to communicate important information in the physical workplace or on the manufacturing floor by merely looking at the visual management tools. Such tools can include information displays such as shadow boards and KPI boards, visual controls, labels and signs, colour coding and other markings instead of written instructions. Visual Management is a fundamental aspect of Lean as it enables companies to identify problems and reinforce standards while ensuring stability and safety in the workplace. When visual management is performed well, it become easy to see and understand the flow of work and how it is progressing. It also benefits the employees as they can clearly see what is expected of them as well as keeping them informed about production status and customer needs.
5S Method
Many lean techniques and principles rely on visual management starting from floor marking using adhesive floor tapes to the large visual displays and scoreboards. Visual management serves as the key sustaining force for many popular lean techniques including 5S which is one of the most fundamental principles in Lean. 5S involves many visual activities that can help create a better work environment. It suggests the use of colours and labels to clearly mark storage locations for each item in the workplace. It also defines inventory levels and reorder triggers to ensure everything is available as needed at the point of use. 5S helps reduce waste by maintaining a systematically organised workspace in which problems immediately become apparent and are thus easy to detect and fix.
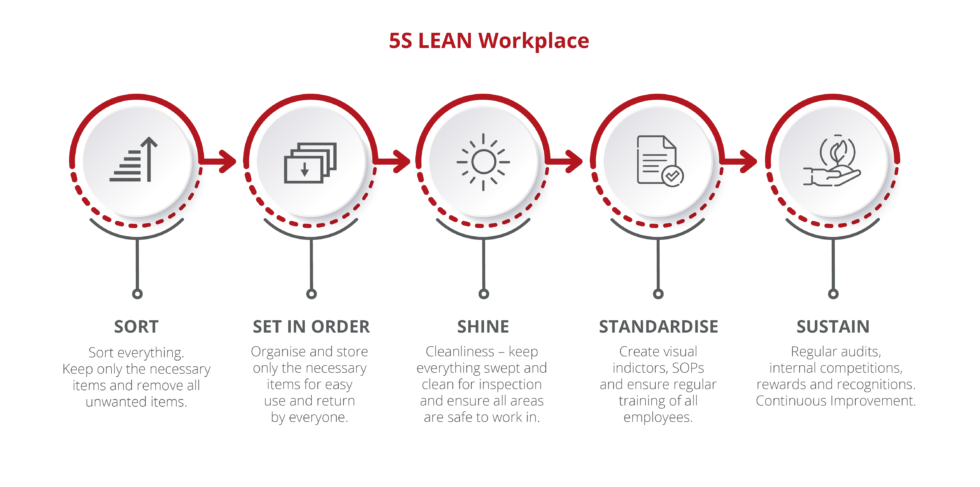
5S consists of five key steps for maintaining an efficient workspace in order to improve the quality of products. 5S was originally a Japanese organisation method composed of five Japanese words: seiri, seiton, seisō, seiketsu, and shitsuke which have been translated as “sort”, “set in order”, “shine”, “standardize”, and “sustain”.
Sort (Seiri) – Seiri is sorting through all items in a location and removing all unnecessary items from the location. Seiri is sorting through all tools, equipment, materials etc. in a location and removing all unnecessary itms from the location. A workplace will be better without unnecessary items or items used infrequently.
Set in Order (Seiton) – Seiton is sorting and organising all tools, equipment etc. in the optimal place for fulfilling their place in the workplace. Signs or other visual tools can help make this more visible.
Shine (Seiso) – Seiso is sweeping or cleaning and inspecting the workplace, tools and machinery on a regular basis. This step also included regular maintenance of the equipment and machinery which helps prevent downtime as potential problems are identified before they occur.
Standarise (Seiketsu) – Seiketsu is to standarise the processes used to sort, order and clean the workplace. It helps ensure that the previous three steps occur regularly and don’t fall by the wayside. Checklists and schedules can help document this.
Sustain/self-discipline (Shitsuke) – Shitsuke is the developed processes by self-discipline of the workers. It helps ensure 5S continues to run smoothly and becomes a long term program and ingrained into the organisations culture.
The Benefits of Visual Management Tools in a 5S Implementation
Research shows that people tend to learn and process information more visually. As the saying goes “A Picture Speaks a Thousand Words”. Therefore, using visual management tools can have a positive impact on safety, productivity, cost, quality, on-time delivery, inventory and equipment reliability. Workplace visuals can also play an important role in job training which will eliminate the need for constant supervision. Employees will quickly identify and react to safety, quality, efficiency problems. In summary, visual management offers the following benefits:
• Clean and Pleasant Workplace
• Creates Self Discipline
• Identifies and eliminate wastes
• Releases Space in the workplace
• Identifies and fixes abnormalities
• Identifies Process issues (like shortage of parts, line imbalance, etc)
• Improves Safety
• Improves Machine Uptime
• Improves Quality
• Improves Employee Morale and Creates Positive Attitude
5S is very simple to understand, but very difficult to Implement. It requires involvement from everyone in the unit – from the Top management to the bottom most layer.
The following are some examples of tools and practices used to aid the organisational efforts of 5S:
Shadow Boards: A shadow board is essentially a backing that is visible when a tool is removed from a pegboard or tool chest. An operator can quickly identify which tools are in use or missing.
Floor Markings: Floor tape can be used to define spaces and create specific spaces for equipment or supplies. Floor marking tape can also be used to help safely guide people to their destination.
Signage: Signage can be used to indicate where tools and equipment are stored as well as to indicate a hazard.
Colour Coding: Colour coding can apply to a variety of areas including tool shadow boards and for floor marking standards. Work boards can also be colour coded which enables employees to keep track of their work tasks and 5S activities.
To conclude, here are some tips to help you create an effective visual management system:
• Always keep in mind the goal which is to make the area more informative.
• Decide where you need to introduce visual management.
• Decide who is going to be involved in the implementation effort.
• Identify the information deficits, determine what needs to be shown and the type of information that need to be communicated.
• Mark floors, add signs, label storage areas, etc. Use the colour standards that are being used consistently in your facility.
• Information has to be easily understandable, concise, accurate, relevant, up-to-date and accessible to everyone. Everyone has to be able to understand the message.
• Create a guide that describes the key elements associated with each visual type.
Want to find out more…
– Contact us today to discuss how our visual management tools could be implemented in your workplace